UiTM JENGKA PAHANG 💖
UED102 (STUDY SKILLS)
Here I am! UiTM Jengka Pahang. Beautiful right?
First of all Assalamualaikum and hello world! Salam UiTM Dihatiku Salam Khazanah Alam 🌲💗 This is my first time using a blog. I created this blog for UED102 Study Skills class. This is one of the tasks in this subject. The tasks is to provide the summaries in each topics that i've learnt in every weeks.
Let me introduce myself first. My name is Ameera Zulaikha Binti Abdul Hamid and I am 18 years old. I am from Kota Bharu, Kelantan. I'm a student who currently study for Diploma in Science (AS120) 2018/2019 session in UiTM Pahang, Jengka Campus.
WEDNESDAY (25 JULY 2018) - 8.00 am
The learning process was held at Al-Farabi which is located in InfraScience-Tech (IST) building and our lecturers are Madam Fadhilah Binti Abdul Hamid and Sir Muhammad Isha Bin Ismail. For this week I learnt about this 3 topics;
🌸 GETTING READY TO LEARN
🌸 GOAL SETTING
🌸TIME MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONAL SKILLS
WHAT IS UED102 ?
UED102 prepares students with learning skills for varsity life. It exposes students to basic academic skills. It would help students to know the professionalities about their own study skills.
INTRODUCTION TO STUDY SKILLS UED102 :
Syllabus Content Alert ! There are 7 topics in this subject;
- GETTING READY TO LEARN
- GOAL SETTING
- TIME MANAGEMENT
- GETTING TO KNOW THE CAMPUS
- MEMORY LEARNING & IMPROVING CONCENTRATION
- TAKING LECTURE NOTES
- ACADEMIC INTEGRITY & PERFORMANCE
But how about the marks?
For Assessment:
- E-Portfolio - (60%)
- Video Presentation - (40%)
TOPIC 1 : GETTING READY TO LEARN 🎓
This topic was lectured by Madam Fadhilah. Lets get started! First and foremost, you need to set in your mind that you are not in school anymore. You really need to have a lot of strength to survive either its mentally or physically in this university life. There are a lot of differences between school life and university life.
- MAKING THE TRANSITION (FROM SCHOOL TO UNIVERSITY)
As we know, school and university are totally different.Making a move from a comfort zones which is school life to university life is not an easy task. You need to make new friends with a different backgrounds, find out new things, adapting yourself to the new environment or lifestyle and many more! So here the differences between school and university life:
VS
SCHOOL |
UNIVERSITY |
You can depend on your teacher |
You have to survive on your own |
Spend more time in class. |
Spend less time in class. |
You should wear your school uniform |
You feel free to wear anything |
Lots of exam. |
Need to read a lot of things but fewer test. |
Your schedule and times table are pack |
You have a lot of free and leisure time |
The teachers will remind them for the upcoming exams. |
The lecture will not bother or remind for the examinations. |
You should wake up early in the morning |
You can wake up whenever you want |
Students attendance will be taken everyday. |
Attendance will not be taken in some classes. |
You are forced to take and learn all the subjects |
You can drop a class |
Students’ finance are managed by their parents. |
Living on your own budget. |
You can live with your parents at home |
You get to live with your friends in college |
Not involving in extra activities |
Involving in so many activities. |
You can study comfortably at home before test |
Library becomes your home away from home |
Lots of homeworks |
Fewer daily assignments that might not be checked |
Maximum 40 students in one class |
Maximum 200 students or more in one class |
NOT TO MENTION! 💢
- You may be living on your own for the first time.
- You may have a job.
- You may be making new friends.
- You may be in relationship.
- You may be in new city.
- You may be involved in lots of extra activities.
- Managing your own finances for the first time
SO HOW DO I STEP UP MY GAME?
- DON'T GET BEHIND ON READING
- LEARN TO GET GOOD NOTES
- TAKE NOTES FROM MISSED CLASSES
- GO TO EVERY CLASS
- GO TO CLASS EARLY
- MAKE A WEEKLY SCHEDULE
- MAKE A MASTER LIST OF ALL ASSIGNMENTS, PROJECTS AND EXAMS FOR THE ENTIRE SEMESTER
- GET TO KNOW YOUR PERSONAL STYLE AND SCHEDULE YOUR CLASSES ACCORDINGLY
- PUT CONCEPT IN YOUR OWN
- GET TO KNOW YOUR INSTRUCTOR
- FIND OUT WHAT TYPE OF LEARNER YOU ARE
- ASK FOR HELP!
- CHARACTERISTICS OF SUCCESSFUL STUDENTS
1. Attend all classes
- can get more knowledges
- responsible for outcomes and experiences
- plus, all the questions in exam are from lectures.
2. Become an active learner
- write the information for a long-term memory.
3. Participate in class
- ask and answer the questions by the lecturers.
4. Get to know lecturers
- try to talk with the lecturers so that we can be comfortable if we have questions to ask.
5. Form study groups with friends.
- we already comfortable with our friends if we want to ask any questions.
6. Stay up to date with your work
- never procrastinate with our work.
7. Be receptive to change
- try a different ways to learn in university.
8. Work hard this semester
- take action to achieve your dreams.
Every students have their own learning style. Knowing our learning styles is very important because can know our possibilities in studies. Madam Fadhilah gave us "Learning Styles Inventory" questions. There are 3 styles of learning. It is VISUAL or AUDITORY or KINESTHETIC modes. Let me explain what is the meaning of that 3 learning styles.
VISUAL : You have strong visualization skills and can remember objects,shapes, and pictures. You learn by reading,and by watching films, videos, and demonstrations. You can see pictures in your mind.
AUDITORY : You have a "good ear" and can hear differences in tones and rhythm. Reading out loud will be beneficial. You can remember what you hear in a lecture.
KINESTHETIC : You are a hands-on learner. You have a good coordination and learn by doing. You generally have an active approach to learning.
TOPIC 2 : GOAL SETTING 🥅
This topic was lectured by Sir Muhammad Isha Bin Ismail. As we started new semester soon, of course all of us have a lot of goals to achieve right?
WHAT IS A GOAL?
GOALS; the object of a person's ambition or effort
; an aim or desired result.
; attainable, measurable, in writing, has time limit (duration),within your control.
Make sure that your goals are :
"LOW EFFORT, BUT HIGH VALUE"
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOALS 🌈
What a goal should be ? A goal should be ” SMART “
S - Smart
M - Measurable
A -
Achievable
R - Realistic
T -
Time based
Other than that :
-
Self chosen
-
Moderately challenging
-
Realistic
-
Specific
-
Positive
MY GOALS🎓
MY ACADEMIC GOALS ✨
- Finishing my studies in 2 years and 6 month with a dean list which I must get 3.50 above in each semester.
- Focus or istiqamah in studies.
- Joining some community work and curiccular within my study period.
- Graduate on time.
- Manage to complete all the assignment that had been given by the lecturers and submit it on time.
MY PERSONAL GOALS ✨
- After I finished my diploma. I want to go to the next level which is degree at the oversea.
- I want to pursue degree in food science.
- Pray early or on time.
- Travel around the world with family or friends.
- Bring my parents to perform Hajj.
- SETTING GOALS FOR THE NEW SEMESTER
- SETTING GOALS FOR THE NEW SEMESTER
- Don't want to PROCRASTINATE anything in all aspects.
- Read some topic before going to class.
- More focus on class so that I will understand more about all the subject.
- Start taking effective notes in the class so I can revise it at college.
- WRITING EFFECTIVE GOAL STATEMENTS
There are 5 steps to write your goals precisely.
STEP 1 : My goals
⇊
STEP 2 : Obstacles
⇊
STEP 3 : Resources available
⇊
STEP 4 : Review and revise
⇊
STEP 5 : Publish goal statement
- USING THE LEARNING MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
3 STEPS TO SUCCESS 😍
- Set the goals
- Make a commitment and hardwork (USAHA+DOA)
- Be accountable (TAWAKAL)
" IF THE PLAN DOESN'T WORK, CHANGE THE PLAN BUT NEVER THE GOAL" -say it louder!!!
TOPIC 3 : TIME MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATION SKILLS ⌚
WHAT IS TIME?

5 STRATEGIES (STUDY SYSTEM)
TASK 1
Make a daily schedule started from (26/7-1/8)
Sir Isha suggested us to use any applications that already had in our own smartphone. So I used calendar from my smartphone!
Here are some of resources that we can find at UiTM Jengka. This topic was lectured by Sir Mohd Isha.
Here I'm dropping some photos of my university!
WHAT IS TIME?
- Time is a stubborn illusion (Albert Einstein)
- Definition: the indefinite continued progress of existing events in the future, past, and present
- Time management: the ability on using time effectively or productively especially work

- OPTIMISING STUDY TIME
5 STRATEGIES (STUDY SYSTEM)
1. Prepare beforehand
2. Take advantage of downtime
3. Take notes while studying
4. Weekly schedule
5. Daily planner
6. Semester calendar
7. Academic vs personal life
8. AVOID PROCRASTINATION!
Reason Procrastination
- Perfectionist
- Avoid failure
- Avoid success
- Being rebellious
- Feeling overwhelmed
- Lazy
Remedy Procrastination
- Go back to your goal
- Alert to deadline
- Prioritized
- Self rewards
- ORGANISING STUDY TIME
ADVANTAGES OF BEING ORGANIZED
- Keep on schedule and meet deadline
- Reduce stress, we in control
- Complete works without stress
- Build your confidence
- USING TIME-MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES TO STAY MOTIVATED
HOW TO MANAGE TIME?
TASK 1
Make a daily schedule started from (26/7-1/8)
Sir Isha suggested us to use any applications that already had in our own smartphone. So I used calendar from my smartphone!
26 JULY 2018
27 JULY 2018
28 JULY 2018
29 JULY 2018
30 JULY 2018
31 JULY 2018
1 AUGUST 2018
TASK 2
LIST DOWN HIGH, MEDIUM, LOW, AND ADDITIONAL PRIORITIZE
- REDUCING PROCRASTINATION
1. Create a to-do list
2. Remove distractions
3. Do one thing at a time
4. Tackle the hard stuff first
5. Reward yourself with breaks
WEDNESDAY (01 AUGUST 2018) - 8.00 am
TOPIC 4 : GETTING TO KNOW THE CAMPUS🏫
Here are some of resources that we can find at UiTM Jengka. This topic was lectured by Sir Mohd Isha.
- MAKING THE MOST OF COLLEGE RESOURCES
TYPE OF RESOURCES
|
EXAMPLES
|
UITM PAHANG, JENGKA CAMPUS
|
Academic Resources
|
Library, Info Tech & Computer,
Registrar
|
Al-Bukhari 1, Al-Bukhari 2, PTAR,
InfraScienceTech (IST), Unit Kaunseling, Al-Razi, Makmal IT, Al-Ghazali
(Bilik Lecturer), Pejabat Bendahari, Hal Ehwal Akademik (HEA)
|
Housing, Dining & Transportation
Resources
|
Buses, Dining Places
|
Housing: Kolej Tok Gajah (KTG), Kolej
Mat Kilau (KMK1&KMK2), Kolej Dato/ Bahaman (KDB), Stesen Bas, Van
Koperasi, Buses.
Dining: Medan Selera, Dewan Makan
Transportation: Unit Kenderaan, Unit
Fasiliti, Unit Kesihatan, Unit Sukan.
|
Student Organization Resources
|
Extra-curricular, Leisure Activities
|
Hal Ehwal Pelajar (HEP), Post Pengawal,
Padang A & B, Court Tennis, Padang Rugby, Court Futsal, Stadium, Kem
Gading, Dataran Integrasi.
|
KOLEJ MAT KILAU 2
POS PENGAWAL
KOLEJ DATO' BAHAMAN
BANGUNAN AL-GHAZALI
KOLEJ TUN TEJA
UNIT FASILITI
BANGUNAN HAL EHWAL AKADEMIK
BANGUNAN INFRASCIENCE TECH
UNIT KENDERAAN
BANGUNAN AL-RAZI
BUSSES
TOPIC 5 : MEMORY LEARNING & IMPROVING CONCENTRATION🌺
This topic was lectured by Sir Muhd Sufyan Bin Mohd Zaki. The sub-topics are:
LEARNING PYRAMID

MEMORY VS BRAIN
 VS
VS 
TWO COMPONENTS MEMORY MODEL
LONG-TERM MEMORY : SUB SYSTEM:
WORKING MEMORY (WM)
LONG-TERM MEMORY (LTM)
WEDNESDAY (08 AUGUST 2018) - 8.00 am
This topic was lectured by Sir Muhd Sufyan Bin Mohd Zaki. The sub-topics are:
- UNDERSTANDING MEMORY PROCESSES
- MEMORY STRATEGIES
- UNDERSTANDING CONCENTRATION
- STRATEGIES FOR IMPROVING CONCENTRATION
- READING / STUDY SYSTEM (SQ3R)
LEARNING PYRAMID
MEMORY VS BRAIN
MEMORY : The retention of information over time (Santrock,2011) or the mind stores and remember information (mental processes/cognition) like computer software. {COMPUTER HARDWARE}
BRAIN : When we learn, and remember, we will encode, store, and retrieve the information. The analogy is like a computer. {COMPUTER SOFTWARE}
MEMORY STRUCTURE
DEFINITION : Capacity to remember, Capacity that permits organisms to benefit from past experiences.
STRUCTURE : Two functional system
- WORKING MEMORY
- LONG-TERM MEMORY
FUNCTIONS : -Storage of information(putting informations in memory)
- System specific functions
LONG-TERM MEMORY : SUB SYSTEM:
- Procedural memory
- Semantic memory
- Episodic memory
WORKING MEMORY
- Phonological loop
- Visuospatial sketchpad
- Central executive
WORKING MEMORY (WM)
DEFINITION
|
Memory system associated with sensory, perceptual, attentional, and
short-term memory processes
|
FUNCTION
|
Enables people to respond according to the demands of a “right now”
situation :
Critical
role in decision making, problem solving movement planning and execution
Interacts
with long-term memory
Retroactive
workspace
|
DURATION
|
Maintains information 20-30 sec. before losing parts of info
|
CAPACITY
|
J
store ~ 7 items (+/- 2)
J
Person can increase capacity by “Chunking”
|
TYPE
|
1. Phonological
: storage of verbal cues/info
2. Visuospatial
sketchpad : visually detected spatial info
3. Cental
executive : coordinate info in WM include retrieve from LTM.
|
LONG-TERM MEMORY (LTM)
DEFINITION
|
More permanent storage repository of information.
|
FUNCTION
|
Allows people to have information about specific past events as well
as general acknowledge
|
DURATION
|
Unknown since we cannot satisfactorily measure duration of info in
LTM.
|
CAPACITY
|
Relatively unlimited
|
TYPE
|
Procedural
: stores information about “how to do” specific activities, e.g. motor
skills.
Semanthic
: Stores our general knowledge about the world based upon experiences, e.g.
concepts
Episodic
: Stores our knowledge about personally experienced events. Allows us to “travel
back in time”.
|
- REMEMBERING AND FORGETTING
🌸 Trace decay
🌸 Proactive interference
🌸 Retroactive interference
THE STEPS
1. Encoding : Process of transforming to-be-remembered information into a form that can be stored in memory
2. Storage : Process of placing information in long-term memory.
3. Rehearsal : Process that enables a person to transfer information from working to long-term memory.
4. Retrieval : Process of searching through LTM for information needed for present use.
WORKING MEMORY PROCESSING OF INFORMATION
- Information processed to allow person to achieve action goal or goal of problem at hand. example;
🌹 remember how to perform an action as just instructed.
🌹 solve a specific movement problem e.g.; how to throw a ball to another person ; how to fit together the process of a puzzle.
MEMORY STRATEGIES
- Strategy to remember e.g. the colours of rainbow or your friends phone number without smartphone or pen or paper.
HOW TO IMPROVE YOUR STRATEGY
- Massed practice vs spaced practice
- Break reading material down
CAUSES OF POOR CONCENTRATION
- Lack of attention
- Lack of interest
- Lack of motivation
- Distraction from others
- Uncomfortable environment
- Psychological matters - illness, tiredness
- Phychologicalmatters - personal problems, worries, anxieties
SQ3R
WHAT IS SQ3R ?
Survey
Question
Read
Recite
Review
WEDNESDAY (08 AUGUST 2018) - 8.00 am
TOPIC 6 : TAKING LECTURE NOTES📝
This topic was lectured by Madam Fadhilah binti Abdul Hamid
- Writing down ideas from lecturers and reading in our own words.
WHY TAKE NOTES?
This topic was lectured by Madam Fadhilah binti Abdul Hamid
- TAKING LECTURE NOTES
- Writing down ideas from lecturers and reading in our own words.
WHY TAKE NOTES?
💥 pay attention in class
💥 study for quiz / tests / final exam
💥 improve our memory
💥 takes ownership of ideas
💥 engage our senses
💥 organize and process data and info
💥helps the lecturers test the student on how well they captured the given info
WHY REVIEW NOTES?
📖 We lose 80% of what we hear during the class if it is now reviewed within a few hours.
📖 Identify any questions for peers, the next class or to ask lecturers
📖 There is not enough time to absorb all the given info in class if it is not reviewed on a regular basis
📖 Think : " If I were tested on this lectures tomorrow, will I answer it? Make it so!"
WHY "RECAPTURE" NOTES AFTER CLASS ?
📸 Frees up to write in quick, shorthand during class
📸 An excellent test-prep strategy for reinforcing info
📸 Better than re-copying, you're digesting and rephrasing
INTRODUCY QUESTION
WHAT MATERIALS DO WE NEED?
✏ loose-leaf paper
✏ binder
✏ folders with pockets
✏ pens
✏ pencils
✏ erasers and etc.
BEFORE CLASSES
📓 Review notes the day before
📓 Review your reading assignment
📓 Make sure you have paper, text, pens/pencils, handout
📓 Write the date at the top of you paper
📓 Leave spaces between the lines so that you can add some important informations later.
PHYSICAL FACTORS
🐰Seating
-near the front and center so that you can have better vision and better hearing
🐰Avoid distraction
- doorways, window glare, peers, and many others
HOW DO WE TAKE NOTES?
⭐ Jot down dates and label notes
⭐ Give ourselves space to write
⭐ Use abbreviations, symbols and acronyms
⭐ Use an outline to show :
-main ideas
- supports
- examples
⭐ Use your own language
SOME EXAMPLES OF ABBREVIATIONS, SYMBOLS, AND ACRONYMS
SYMBOLS
!! - IMPORTANT
?? - NOT UNDERSTAND
** - ADDED INFORMATION
ABBREVIATION & ACRONYMS
BRB - BE RIGHT BACK
OTW - ON THE WAY
BTW - BY THE WAY
IKR - I KNOW RIGHT
TBH - TO BE HONEST
HOW DO WE PREPARE FOR CLASS?
💢 Do pre-reading and homework
💢 Review syllabus
💢 Review previous notes
💢Look-up keywords from the slides
💢Plan on listening 80% at the time and another 20% on writing
WHILE TAKING NOTES!
🐳Be an aggresive, not a passiive listener
🐳Ask questions and discuss if its permitted
- Seek out the meaning
MOOD OF LECTURERS
💘 Observation is key
- Keen observers focus their attention on the details and make the most of their time during letures by preparing and reviewing BEFORE THE LECTURES EVEN STARTS!
KEY ACTIONS TO NOTE AS YOU OBSERVED YOUR INFO.
👉 Be alert to repetition
- When an instructor repeats a specific points, make a note of it!
👉 Watch the board or overhead projector
- If an instuctor writes something down, the material is important!
👉 Notice the instructor's interest level
- If the instuctor is excited about something, it is likely to be on an exam
👉 Let go of judgements about lecture styles
- Just follow the flow and be comfortable using that kind of learning styles.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOUR INSTRUCTOR ISN'T TOO INTERESTING?
😎 Sit in front of the row
*board is easier to read
*the instructor can see you easily
THERE ARE SOME STRATEGIES OF TAKING NOTES!
First, CORNELL NOTE TAKING.

Second, TWO COLUMN METHOD.

Third, OUTLINING

Fourth, MAPPING METHOD
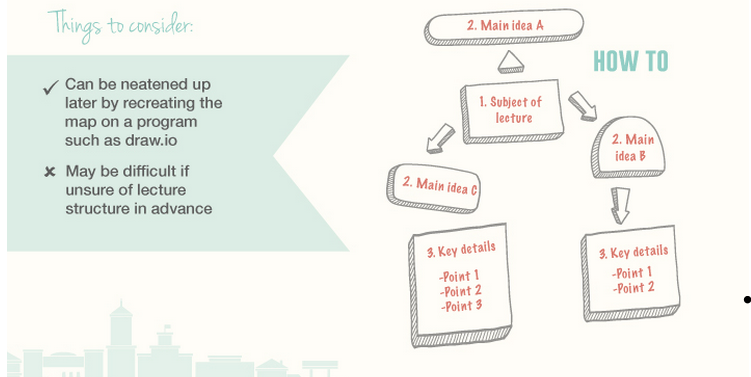
Fifth, SENTENCE METHOD

HOW DO WE REVIEW AFTER CLASS?
💎 Review notes along with the book
-💎 Create our own examples
💎 Discuss and compare notes with others
💎 Re-write notes
💎 Practice those skills you wish to develop
💎 Ask for clarification
REMEMBER SQ4R

- Survey : Overview; quick scan
- Question : establish a purpose
- Read : to answer questions
- Rite : take notes
- Review : at the short, intervals
- Recite : answer to questions with the book closed
TOPIC 7 : ACADEMIC INTEGRITY AND PERFORMANCE🚨
This topic was lectured by Sir Muhd Sufyan Bin Muhd Zaki.

HOW TO PREVENT PLAGIARISM
STEP 1 : Planning paper
- consult lecturers
- plan your paper
- take effective notes
STEP 2 : Writing your paper
- cite your sources
- make it clear
- know how to paraphase
- evaluate your sources
- include a references pages


ACADEMIC STATUS
CALCULATING THE CGPA
So yass that's all from me sharing the summaries from the topics that I've learnt during my UED102 class. Not to forget thank you soooo much to the lecturers Sir Isha, Madam Fadhilah and Sir Sufyan ! Finally Interim Weeks is ended! Alhamdulillah. See yah when I see yah! XOXO! 😘

💥 study for quiz / tests / final exam
💥 improve our memory
💥 takes ownership of ideas
💥 engage our senses
💥 organize and process data and info
💥helps the lecturers test the student on how well they captured the given info
WHY REVIEW NOTES?
📖 We lose 80% of what we hear during the class if it is now reviewed within a few hours.
📖 Identify any questions for peers, the next class or to ask lecturers
📖 There is not enough time to absorb all the given info in class if it is not reviewed on a regular basis
📖 Think : " If I were tested on this lectures tomorrow, will I answer it? Make it so!"
WHY "RECAPTURE" NOTES AFTER CLASS ?
📸 Frees up to write in quick, shorthand during class
📸 An excellent test-prep strategy for reinforcing info
📸 Better than re-copying, you're digesting and rephrasing
INTRODUCY QUESTION
WHAT MATERIALS DO WE NEED?
✏ loose-leaf paper
✏ binder
✏ folders with pockets
✏ pens
✏ pencils
✏ erasers and etc.
BEFORE CLASSES
📓 Review notes the day before
📓 Review your reading assignment
📓 Make sure you have paper, text, pens/pencils, handout
📓 Write the date at the top of you paper
📓 Leave spaces between the lines so that you can add some important informations later.
PHYSICAL FACTORS
🐰Seating
-near the front and center so that you can have better vision and better hearing
🐰Avoid distraction
- doorways, window glare, peers, and many others
HOW DO WE TAKE NOTES?
⭐ Jot down dates and label notes
⭐ Give ourselves space to write
⭐ Use abbreviations, symbols and acronyms
⭐ Use an outline to show :
-main ideas
- supports
- examples
⭐ Use your own language
SOME EXAMPLES OF ABBREVIATIONS, SYMBOLS, AND ACRONYMS
SYMBOLS
!! - IMPORTANT
?? - NOT UNDERSTAND
** - ADDED INFORMATION
ABBREVIATION & ACRONYMS
BRB - BE RIGHT BACK
OTW - ON THE WAY
BTW - BY THE WAY
IKR - I KNOW RIGHT
TBH - TO BE HONEST
HOW DO WE PREPARE FOR CLASS?
💢 Do pre-reading and homework
💢 Review syllabus
💢 Review previous notes
💢Look-up keywords from the slides
💢Plan on listening 80% at the time and another 20% on writing
WHILE TAKING NOTES!
🐳Be an aggresive, not a passiive listener
🐳Ask questions and discuss if its permitted
- Seek out the meaning
MOOD OF LECTURERS
💘 Observation is key
- Keen observers focus their attention on the details and make the most of their time during letures by preparing and reviewing BEFORE THE LECTURES EVEN STARTS!
KEY ACTIONS TO NOTE AS YOU OBSERVED YOUR INFO.
👉 Be alert to repetition
- When an instructor repeats a specific points, make a note of it!
👉 Watch the board or overhead projector
- If an instuctor writes something down, the material is important!
👉 Notice the instructor's interest level
- If the instuctor is excited about something, it is likely to be on an exam
👉 Let go of judgements about lecture styles
- Just follow the flow and be comfortable using that kind of learning styles.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOUR INSTRUCTOR ISN'T TOO INTERESTING?
😎 Sit in front of the row
*board is easier to read
*the instructor can see you easily
- EFFECTIVE NOTE-TAKING SYSTEM
THERE ARE SOME STRATEGIES OF TAKING NOTES!
First, CORNELL NOTE TAKING.

Second, TWO COLUMN METHOD.

Third, OUTLINING
Fourth, MAPPING METHOD

Fifth, SENTENCE METHOD
HOW DO WE REVIEW AFTER CLASS?
💎 Review notes along with the book
-💎 Create our own examples
💎 Discuss and compare notes with others
💎 Re-write notes
💎 Practice those skills you wish to develop
💎 Ask for clarification
REMEMBER SQ4R
- Survey : Overview; quick scan
- Question : establish a purpose
- Read : to answer questions
- Rite : take notes
- Review : at the short, intervals
- Recite : answer to questions with the book closed
TOPIC 7 : ACADEMIC INTEGRITY AND PERFORMANCE🚨
This topic was lectured by Sir Muhd Sufyan Bin Muhd Zaki.
- AVOIDING PLAGIARISM
WHAT IS PLAGIARISM
- Plagiarism is an act of using or copying the other author without citation or crediting to the author.
HOW TO PREVENT PLAGIARISM
STEP 1 : Planning paper
- consult lecturers
- plan your paper
- take effective notes
STEP 2 : Writing your paper
- cite your sources
- make it clear
- know how to paraphase
- evaluate your sources
- include a references pages
- CALCULATING GRADE POINT AVERAGE
GPA is GRADE POINT AVERAGE,
CGPA is CUMMULATIVE GRADE POINT AVERAGE
HOW TO CALCULATE ?
ACADEMIC STATUS
CALCULATING THE CGPA
ACTIVITY 1
So yass that's all from me sharing the summaries from the topics that I've learnt during my UED102 class. Not to forget thank you soooo much to the lecturers Sir Isha, Madam Fadhilah and Sir Sufyan ! Finally Interim Weeks is ended! Alhamdulillah. See yah when I see yah! XOXO! 😘






























